Over the years we’ve all become aware of the threats we face from allowing the use of removable media and portable devices in a computer environment. These threats have been around for a long time. You can look back to the “Agent.BTZ” USB worm attack on the U.S. Military in 2008, “USB Thief” trojan discovered in 2016, or even the more recent FBI reports over the last two years on the “BadUSB” attack. The BadUSB attack was completed by mailing USB media to victims across all industries that used social engineering to have them connect the ransomware delivering devices to their computers.
That is a short list, from a very long list, of known removable media attacks, but just one of those should be enough to make you rethink your security posture related to these devices. There is still a surprisingly large number of organizations that take the blind trust approach to this continued and evolving threat. Relying on end user education and use policy will likely fail you. So, what’s a solution that can be leveraged in a modern zero trust security framework? Let’s take a look at the simplicity offered by using Microsoft Windows Group Policy Objects (GPO) settings.
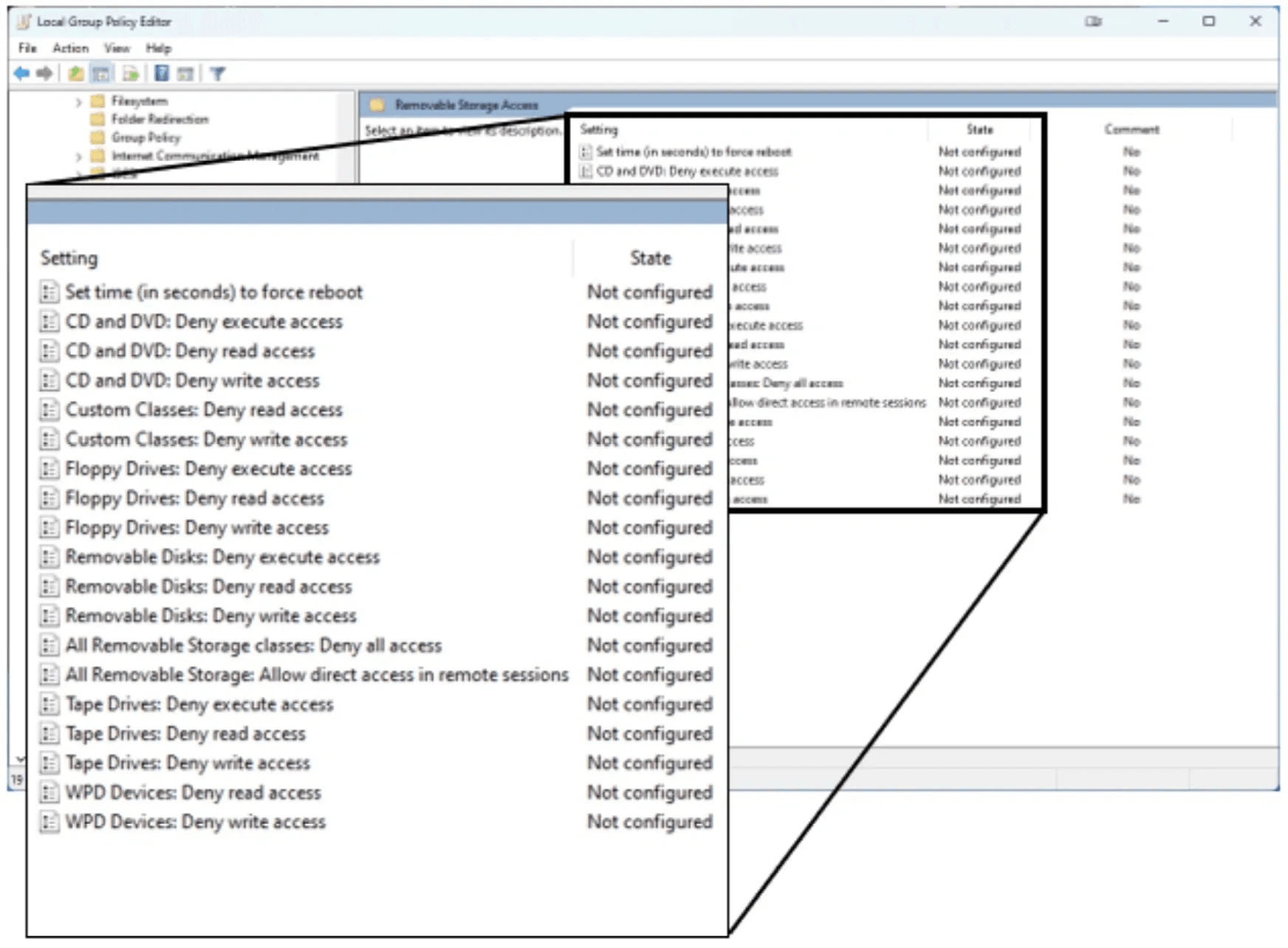
Restricting removable media usage on an endpoint within a domain is a core security control that administrators must implement. It may come as a surprise that many administrators do not realize that this functionality can be implemented entirely within a Group Policy (GPO) and that third party tools are not required. GPOs managing removable media can be configured for both user and computer objects for a variety of storage media (USB, CD, floppy, tape drives, windows portable devices, etc.). Policies consist of allowing or denying read, write, and execute access for the various media types. A complete list of options can be seen in the image below.